Abstract
A simulation framework improves autonomous driving by generating diverse, high-fidelity driving scenarios, leading to better generalization and robustness in real-world testing.
Achieving fully autonomous driving systems requires learning rational decisions in a wide span of scenarios, including safety-critical and out-of-distribution ones. However, such cases are underrepresented in real-world corpus collected by human experts. To complement for the lack of data diversity, we introduce a novel and scalable simulation framework capable of synthesizing massive unseen states upon existing driving logs. Our pipeline utilizes advanced neural rendering with a reactive environment to generate high-fidelity multi-view observations controlled by the perturbed ego trajectory. Furthermore, we develop a pseudo-expert trajectory generation mechanism for these newly simulated states to provide action supervision. Upon the synthesized data, we find that a simple co-training strategy on both real-world and simulated samples can lead to significant improvements in both robustness and generalization for various planning methods on challenging real-world benchmarks, up to +6.8 EPDMS on navhard and +2.9 on navtest. More importantly, such policy improvement scales smoothly by increasing simulation data only, even without extra real-world data streaming in. We further reveal several crucial findings of such a sim-real learning system, which we term SimScale, including the design of pseudo-experts and the scaling properties for different policy architectures. Our simulation data and code would be released.
Community
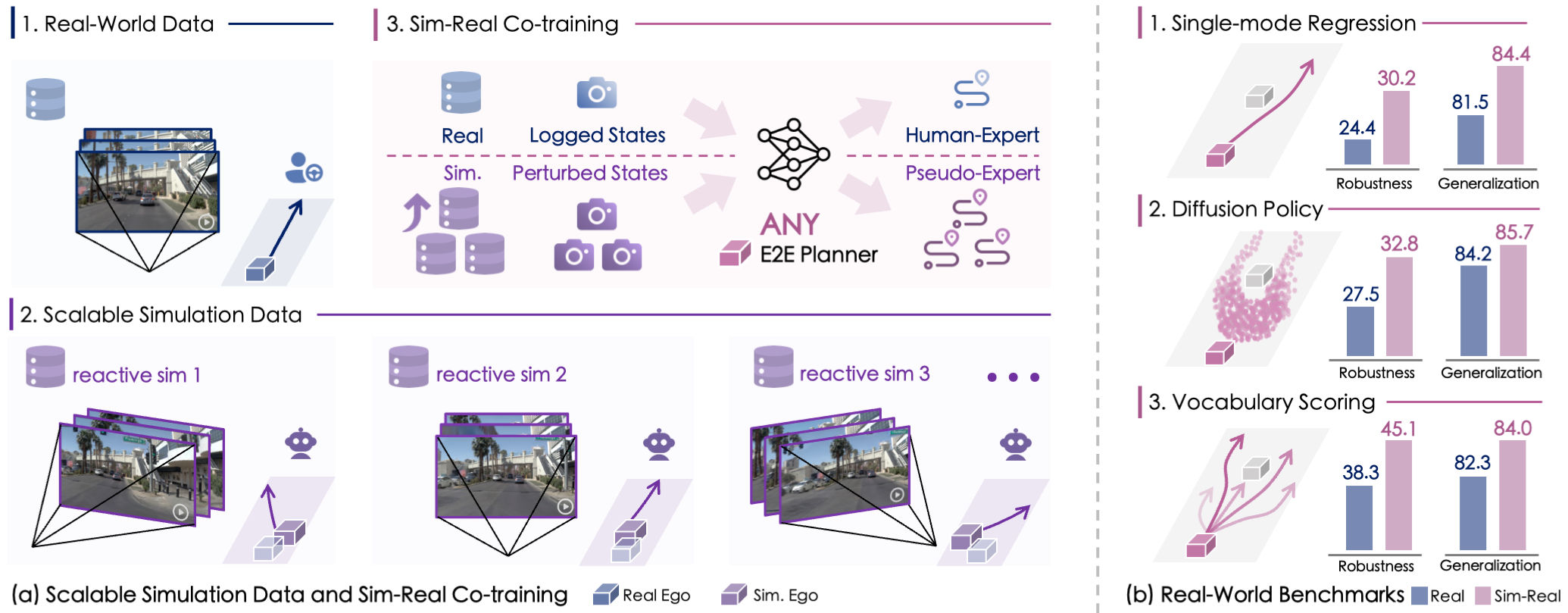
- 🏗️ A scalable simulation pipepline that synthesizes diverse and high-fidelity reactive driving scenarios with pseudo-expert demonstrations.
- 🚀 An effective sim-real co-training strategy that improves robustness and generalization synergistically across various end-to-end planners.
- 🔬 A comprehensive recipe that reveals crucial insights into the underlying scaling properties of sim-real learning systems for end-to-end autonomy.
📜 [technical report]
🏠 [project page]
📑 [github]
This is an automated message from the Librarian Bot. I found the following papers similar to this paper.
The following papers were recommended by the Semantic Scholar API
- WPT: World-to-Policy Transfer via Online World Model Distillation (2025)
- ZTRS: Zero-Imitation End-to-end Autonomous Driving with Trajectory Scoring (2025)
- RoaD: Rollouts as Demonstrations for Closed-Loop Supervised Fine-Tuning of Autonomous Driving Policies (2025)
- SPACeR: Self-Play Anchoring with Centralized Reference Models (2025)
- Model-Based Policy Adaptation for Closed-Loop End-to-End Autonomous Driving (2025)
- nuPlan-R: A Closed-Loop Planning Benchmark for Autonomous Driving via Reactive Multi-Agent Simulation (2025)
- DriveCritic: Towards Context-Aware, Human-Aligned Evaluation for Autonomous Driving with Vision-Language Models (2025)
Please give a thumbs up to this comment if you found it helpful!
If you want recommendations for any Paper on Hugging Face checkout this Space
You can directly ask Librarian Bot for paper recommendations by tagging it in a comment:
@librarian-bot
recommend
Models citing this paper 0
No model linking this paper
Datasets citing this paper 0
No dataset linking this paper
Spaces citing this paper 0
No Space linking this paper
Collections including this paper 0
No Collection including this paper
