---
library_name: transformers
license: apache-2.0
pipeline_tag: text-generation
base_model: Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct
tags:
- quantized
- w4a16
- llm-compressor
---
```
██╗ ██╗██╗ ██╗ █████╗ ██╗ ██████╗
██║ ██║██║ ██║██╔══██╗███║██╔════╝
██║ █╗ ██║███████║███████║╚██║███████╗
██║███╗██║╚════██║██╔══██║ ██║██╔═══██╗
╚███╔███╔╝ ██║██║ ██║ ██║╚██████╔╝
╚══╝╚══╝ ╚═╝╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚═════╝
🗜️ COMPRESSED & OPTIMIZED 🚀
```
# Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct - W4A16 Quantized
W4A16 (4-bit weights, 16-bit activations) quantized version of Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct using **LLM-Compressor**.
- 🗜️ **Memory**: ~75% reduction vs FP16
- 🚀 **Speed**: Faster inference on supported hardware
- 🔗 **Original model**: [link]
Click to view compression config
```python
from datasets import load_dataset
from llmcompressor.modifiers.quantization import GPTQModifier
from llmcompressor import oneshot
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
# Load model with memory management
model_stub = "Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct"
model_name = model_stub.split("/")[-1]
# Use conservative parameters
num_samples = 1024
max_seq_len = 8192
print(f"Loading model: {model_stub}")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_stub,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto",
max_memory={0: "22GB", 1: "22GB", "cpu": "24GB"},
)
print("Loading tokenizer...")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_stub)
print("Loading calibration dataset...")
def preprocess_fn(example):
return {"text": tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
example["messages"],
add_generation_prompt=False,
tokenize=False
)}
# Load dataset and preprocess
ds = load_dataset("neuralmagic/LLM_compression_calibration", split=f"train[:{num_samples}]")
ds = ds.map(preprocess_fn)
ds = ds.shuffle(seed=42)
# Tokenize the dataset
def tokenize(sample):
return tokenizer(
sample["text"],
padding=False,
max_length=max_seq_len,
truncation=True,
add_special_tokens=False,
)
print("Tokenizing dataset...")
ds = ds.map(tokenize, remove_columns=ds.column_names)
# Configure GPTQ with proper Qwen3 MoE ignore patterns
print("Configuring quantization recipe...")
recipe = GPTQModifier(
targets="Linear",
scheme="W4A16",
ignore=["lm_head", "re:.*mlp.gate$"], # Qwen3 MoE pattern (no shared experts)
dampening_frac=0.01,
# Remove sequential_targets - let llmcompressor handle automatically
)
# Apply quantization
print("Starting quantization process...")
oneshot(
model=model,
dataset=ds,
recipe=recipe,
max_seq_length=max_seq_len,
num_calibration_samples=num_samples,
)
# Save quantized model
save_path = model_name + "-gptq-w4a16"
print(f"Saving model to: {save_path}")
model.save_pretrained(save_path, save_compressed=True)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_path)
print("Quantization completed successfully!")
```
---
## 📄 Original Model README
# Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct
 ## Highlights
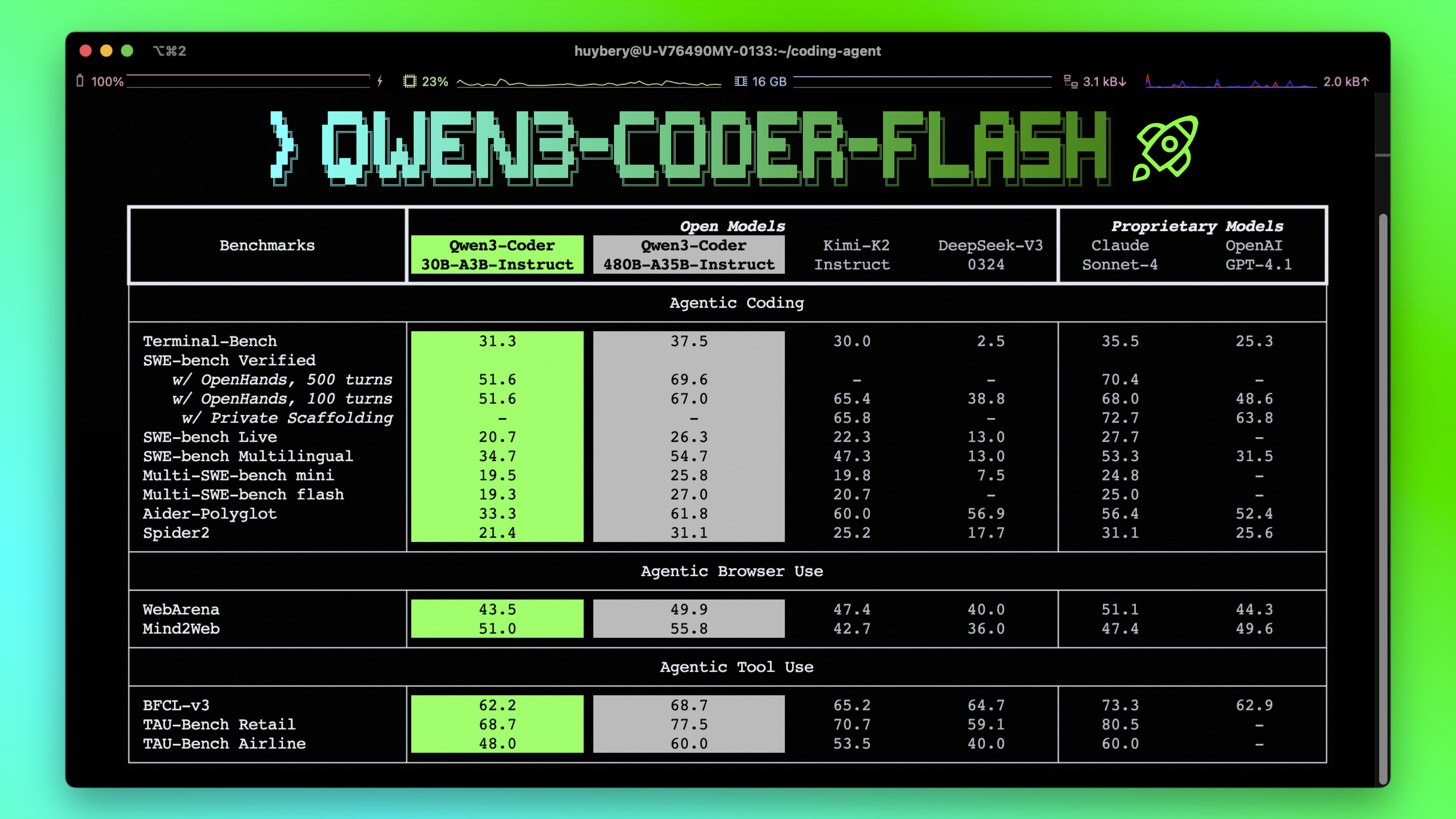
**Qwen3-Coder** is available in multiple sizes. Today, we're excited to introduce **Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct**. This streamlined model maintains impressive performance and efficiency, featuring the following key enhancements:
- **Significant Performance** among open models on **Agentic Coding**, **Agentic Browser-Use**, and other foundational coding tasks.
- **Long-context Capabilities** with native support for **256K** tokens, extendable up to **1M** tokens using Yarn, optimized for repository-scale understanding.
- **Agentic Coding** supporting for most platform such as **Qwen Code**, **CLINE**, featuring a specially designed function call format.
## Model Overview
**Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct** has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 30.5B in total and 3.3B activated
- Number of Layers: 48
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 4 for KV
- Number of Experts: 128
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Context Length: **262,144 natively**.
**NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate ```` blocks in its output. Meanwhile, specifying `enable_thinking=False` is no longer required.**
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our [blog](https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen3-coder/), [GitHub](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-Coder), and [Documentation](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
## Quickstart
We advise you to use the latest version of `transformers`.
With `transformers<4.51.0`, you will encounter the following error:
```
KeyError: 'qwen3_moe'
```
The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Write a quick sort algorithm."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=65536
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)
```
**Note: If you encounter out-of-memory (OOM) issues, consider reducing the context length to a shorter value, such as `32,768`.**
For local use, applications such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX-LM, llama.cpp, and KTransformers have also supported Qwen3.
## Agentic Coding
Qwen3-Coder excels in tool calling capabilities.
You can simply define or use any tools as following example.
```python
# Your tool implementation
def square_the_number(num: float) -> dict:
return num ** 2
# Define Tools
tools=[
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name": "square_the_number",
"description": "output the square of the number.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"required": ["input_num"],
"properties": {
'input_num': {
'type': 'number',
'description': 'input_num is a number that will be squared'
}
},
}
}
}
]
import OpenAI
# Define LLM
client = OpenAI(
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API
base_url='http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
api_key="EMPTY"
)
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'square the number 1024'}]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages,
model="Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct",
max_tokens=65536,
tools=tools,
)
print(completion.choice[0])
```
## Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
1. **Sampling Parameters**:
- We suggest using `temperature=0.7`, `top_p=0.8`, `top_k=20`, `repetition_penalty=1.05`.
2. **Adequate Output Length**: We recommend using an output length of 65,536 tokens for most queries, which is adequate for instruct models.
### Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
```
@misc{qwen3technicalreport,
title={Qwen3 Technical Report},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.09388},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388},
}
```
## Highlights
**Qwen3-Coder** is available in multiple sizes. Today, we're excited to introduce **Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct**. This streamlined model maintains impressive performance and efficiency, featuring the following key enhancements:
- **Significant Performance** among open models on **Agentic Coding**, **Agentic Browser-Use**, and other foundational coding tasks.
- **Long-context Capabilities** with native support for **256K** tokens, extendable up to **1M** tokens using Yarn, optimized for repository-scale understanding.
- **Agentic Coding** supporting for most platform such as **Qwen Code**, **CLINE**, featuring a specially designed function call format.

## Model Overview
**Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct** has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 30.5B in total and 3.3B activated
- Number of Layers: 48
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 4 for KV
- Number of Experts: 128
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Context Length: **262,144 natively**.
**NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate ```` blocks in its output. Meanwhile, specifying `enable_thinking=False` is no longer required.**
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our [blog](https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen3-coder/), [GitHub](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-Coder), and [Documentation](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
## Quickstart
We advise you to use the latest version of `transformers`.
With `transformers<4.51.0`, you will encounter the following error:
```
KeyError: 'qwen3_moe'
```
The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Write a quick sort algorithm."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=65536
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)
```
**Note: If you encounter out-of-memory (OOM) issues, consider reducing the context length to a shorter value, such as `32,768`.**
For local use, applications such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX-LM, llama.cpp, and KTransformers have also supported Qwen3.
## Agentic Coding
Qwen3-Coder excels in tool calling capabilities.
You can simply define or use any tools as following example.
```python
# Your tool implementation
def square_the_number(num: float) -> dict:
return num ** 2
# Define Tools
tools=[
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name": "square_the_number",
"description": "output the square of the number.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"required": ["input_num"],
"properties": {
'input_num': {
'type': 'number',
'description': 'input_num is a number that will be squared'
}
},
}
}
}
]
import OpenAI
# Define LLM
client = OpenAI(
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API
base_url='http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
api_key="EMPTY"
)
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'square the number 1024'}]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages,
model="Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct",
max_tokens=65536,
tools=tools,
)
print(completion.choice[0])
```
## Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
1. **Sampling Parameters**:
- We suggest using `temperature=0.7`, `top_p=0.8`, `top_k=20`, `repetition_penalty=1.05`.
2. **Adequate Output Length**: We recommend using an output length of 65,536 tokens for most queries, which is adequate for instruct models.
### Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
```
@misc{qwen3technicalreport,
title={Qwen3 Technical Report},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.09388},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388},
}
``` ## Highlights
**Qwen3-Coder** is available in multiple sizes. Today, we're excited to introduce **Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct**. This streamlined model maintains impressive performance and efficiency, featuring the following key enhancements:
- **Significant Performance** among open models on **Agentic Coding**, **Agentic Browser-Use**, and other foundational coding tasks.
- **Long-context Capabilities** with native support for **256K** tokens, extendable up to **1M** tokens using Yarn, optimized for repository-scale understanding.
- **Agentic Coding** supporting for most platform such as **Qwen Code**, **CLINE**, featuring a specially designed function call format.

## Model Overview
**Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct** has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 30.5B in total and 3.3B activated
- Number of Layers: 48
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 4 for KV
- Number of Experts: 128
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Context Length: **262,144 natively**.
**NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate ``
## Highlights
**Qwen3-Coder** is available in multiple sizes. Today, we're excited to introduce **Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct**. This streamlined model maintains impressive performance and efficiency, featuring the following key enhancements:
- **Significant Performance** among open models on **Agentic Coding**, **Agentic Browser-Use**, and other foundational coding tasks.
- **Long-context Capabilities** with native support for **256K** tokens, extendable up to **1M** tokens using Yarn, optimized for repository-scale understanding.
- **Agentic Coding** supporting for most platform such as **Qwen Code**, **CLINE**, featuring a specially designed function call format.

## Model Overview
**Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct** has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 30.5B in total and 3.3B activated
- Number of Layers: 48
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 4 for KV
- Number of Experts: 128
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Context Length: **262,144 natively**.
**NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate ``