Commit
·
09e2bc4
1
Parent(s):
a0d91e2
Enhance visualization support and update project documentation
Browse filesAdded example visualizations and integrated PandasAI-based chart generation into the application workflow. Updated README with detailed project structure, installation, usage, and visualization support. Included minor code refactoring and logging enhancements, along with configuration adjustments for tool chaining and debugging.
- .idea/misc.xml +1 -1
- .idea/query_mcp_server.iml +1 -1
- README.md +155 -73
- exports/charts/temp_chart_5252d436-6dfe-46e3-a348-49308898940d.png +0 -0
- exports/charts/temp_chart_70308ee4-1919-43a6-b30a-c7024fb0440e.png +0 -0
- exports/charts/temp_chart_730e3451-365a-4a3f-9c4b-d95f991c4bbd.png +0 -0
- exports/charts/temp_chart_7ee5d17e-a9a1-40e1-ab90-cc48a82ef03e.png +0 -0
- exports/charts/temp_chart_91edd69e-ff3b-49e5-834b-399d57898523.png +0 -0
- exports/charts/temp_chart_d2455884-7b1b-4dd5-8e9a-8d928ec9628b.png +0 -0
- gradio_app.py +12 -12
- langchain_mcp_client.py +4 -0
- pandasai_visualization.py +4 -4
- postgre_mcp_server.py +43 -34
- visualization_output.png +0 -0
.idea/misc.xml
CHANGED
|
@@ -3,5 +3,5 @@
|
|
| 3 |
<component name="Black">
|
| 4 |
<option name="sdkName" value="pyfapi_update" />
|
| 5 |
</component>
|
| 6 |
-
<component name="ProjectRootManager" version="2" project-jdk-name="
|
| 7 |
</project>
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
<component name="Black">
|
| 4 |
<option name="sdkName" value="pyfapi_update" />
|
| 5 |
</component>
|
| 6 |
+
<component name="ProjectRootManager" version="2" project-jdk-name="mcp-vis" project-jdk-type="Python SDK" />
|
| 7 |
</project>
|
.idea/query_mcp_server.iml
CHANGED
|
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
|
| 4 |
<content url="file://$MODULE_DIR$">
|
| 5 |
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/.idea/dataSources" />
|
| 6 |
</content>
|
| 7 |
-
<orderEntry type="jdk" jdkName="
|
| 8 |
<orderEntry type="sourceFolder" forTests="false" />
|
| 9 |
</component>
|
| 10 |
</module>
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
<content url="file://$MODULE_DIR$">
|
| 5 |
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/.idea/dataSources" />
|
| 6 |
</content>
|
| 7 |
+
<orderEntry type="jdk" jdkName="mcp-vis" jdkType="Python SDK" />
|
| 8 |
<orderEntry type="sourceFolder" forTests="false" />
|
| 9 |
</component>
|
| 10 |
</module>
|
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,108 +1,190 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
-
A PostgreSQL
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
-
* Natural Language to SQL Translation
|
| 8 |
-
* Live Interaction with PostgreSQL via MCP Protocol
|
| 9 |
-
* Tool Integration with Database Metadata
|
| 10 |
-
* In-Session Conversational Memory
|
| 11 |
-
* Supports multiple LLM clients (Langchain and Smolagents)
|
| 12 |
-
* Gradio web interface for easy interaction
|
| 13 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
|-------------|------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|
|
| 19 |
-
| LLM Framework | [LangChain](https://www.langchain.com/) | Manages agent behavior, memory, and tool interaction |
|
| 20 |
-
| LLM Provider | Google Gemini (via LangChain) | Converts natural language into SQL queries |
|
| 21 |
-
| Agent Runtime | LangGraph’s `create_react_agent` | Runs the ReAct-style LLM agent |
|
| 22 |
-
| Communication | Modular Command Protocol (MCP) | Handles communication between client and PostgreSQL backend|
|
| 23 |
-
| Tooling | `langchain_mcp_adapters` | Loads and manages tools for the agent |
|
| 24 |
-
| Database | PostgreSQL | Serves queried data |
|
| 25 |
-
| UI (optional) | [Gradio](https://www.gradio.app/) | Provides a lightweight web interface for querying |
|
| 26 |
-
| Memory | `FileChatMessageHistory` | Stores short-term in-session memory for conversation context |
|
| 27 |
-
| Language | Python 3.10+ | Core programming language used for development |
|
| 28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 35 |
```bash
|
| 36 |
-
git clone
|
| 37 |
cd query_mcp_server
|
|
|
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
-
2. **Create and
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
```bash
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
-
3. **Install
|
| 46 |
```bash
|
| 47 |
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
|
|
|
| 48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 49 |
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
## Configuration
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
|
| 55 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 56 |
|
| 57 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 58 |
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
|
|
|
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
|
| 66 |
-
##
|
| 67 |
|
|
|
|
| 68 |
|
| 69 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 70 |
|
| 71 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 72 |
|
| 73 |
-
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
|
|
|
|
| 76 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 77 |
|
| 78 |
## Project Structure
|
| 79 |
|
| 80 |
```
|
| 81 |
-
.
|
| 82 |
-
├──
|
| 83 |
-
├── langchain_mcp_client.py
|
| 84 |
-
├──
|
| 85 |
-
├──
|
| 86 |
-
├──
|
| 87 |
-
├──
|
| 88 |
-
├──
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
├── utils.py # Helper functions: intent classification, output parsing, etc.
|
| 91 |
-
├── .env.sample # Template for your environment config
|
| 92 |
-
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
|
| 93 |
-
└── README.md
|
| 94 |
```
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
### Work In Progress (WIP) Notes
|
| 97 |
-
* postgre_mcp_client.py:
|
| 98 |
-
- needs improvement in build_prompt() function
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
* postgre_smolagent_client.py:
|
| 101 |
-
|
| 102 |
-
- Doesn’t support memory yet
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
- Uses a different output format — not yet compatible with parse_mcp_output()
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
- Also needs build_prompt() logic finalized
|
| 107 |
-
* gradio_app.py:
|
| 108 |
-
- Doesn't support conversation chat ui
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Natural Language SQL Query Agent with Visualization
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
+
A PostgreSQL-based query system that converts natural language requests into SQL queries, executes them, and provides visualizations using PandasAI. Built with LangChain, FastMCP, and Gradio.
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
+

|
| 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
+
## Description
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
+
This project combines several components to create a powerful natural language interface to PostgreSQL databases with visualization capabilities:
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
+
### Core Components:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
+
1. **PostgreSQL MCP Server** (`postgre_mcp_server.py`):
|
| 15 |
+
- Handles database connections and query execution
|
| 16 |
+
- Provides tools for table listing, schema retrieval
|
| 17 |
+
- Implements visualization using PandasAI
|
| 18 |
+
- Manages database lifecycle and connection pooling
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
+
2. **LangChain Client** (`langchain_mcp_client.py`):
|
| 21 |
+
- Converts natural language to SQL using LLM
|
| 22 |
+
- Manages conversation history
|
| 23 |
+
- Integrates with MCP tools
|
| 24 |
+
- Handles agent execution flow
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
3. **Gradio Interface** (`gradio_app.py`):
|
| 27 |
+
- Provides web-based chat interface
|
| 28 |
+
- Handles user interactions
|
| 29 |
+
- Displays query results and visualizations
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
+
4. **Memory Management** (`conversation_memory.py`):
|
| 32 |
+
- Implements conversation history persistence
|
| 33 |
+
- Tracks tool usage and queries
|
| 34 |
+
- Manages session state
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
+
5. **Utilities** (`utils.py`):
|
| 37 |
+
- Provides helper functions for output parsing
|
| 38 |
+
- Handles MCP response formatting
|
| 39 |
+
- Manages logging
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
+
6. **Visualization** (`pandasai_visualization.py` and MCP Tools):
|
| 42 |
+
- Implements PandasAI integration for intelligent chart generation
|
| 43 |
+
- Custom MCP tool `visualize_results` that:
|
| 44 |
+
* Takes query results as JSON and a visualization prompt
|
| 45 |
+
* Uses PandasAI to automatically generate appropriate visualizations
|
| 46 |
+
* Saves charts in the `exports/charts/` directory
|
| 47 |
+
- Supports various chart types (bar charts, line plots, pie charts, etc.)
|
| 48 |
+
- Intelligent prompt-based visualization selection
|
| 49 |
+
- Includes standalone testing script:
|
| 50 |
+
* Located at `pandasai_visualization.py`
|
| 51 |
+
* Can be run directly to test PandasAI functionality
|
| 52 |
+
* Creates sample data and generates test visualizations
|
| 53 |
+
* Usage: `python pandasai_visualization.py`
|
| 54 |
+
* Helps verify PandasAI setup and API key configuration
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
## Installation
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
1. **Clone the Repository:**
|
| 59 |
```bash
|
| 60 |
+
git clone <repository-url>
|
| 61 |
cd query_mcp_server
|
| 62 |
+
```
|
| 63 |
|
| 64 |
+
2. **Create and Activate Virtual Environment:**
|
|
|
|
| 65 |
```bash
|
| 66 |
+
python -m venv venv
|
| 67 |
+
source venv/bin/activate # On Linux/Mac
|
| 68 |
+
# or
|
| 69 |
+
.\venv\Scripts\activate # On Windows
|
| 70 |
+
```
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
+
3. **Install Dependencies:**
|
| 73 |
```bash
|
| 74 |
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
| 75 |
+
```
|
| 76 |
|
| 77 |
+
4. **Configure Environment Variables:**
|
| 78 |
+
Create a `.env` file in the project root with the following variables:
|
| 79 |
+
```
|
| 80 |
+
# Database Configuration
|
| 81 |
+
DB_URL=postgresql://username:password@localhost:5432/your_database
|
| 82 |
+
DB_SCHEMA=public
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
# Test the PandasAI Setup (Optional)
|
| 85 |
+
# Before running the main application, you can test the visualization component:
|
| 86 |
+
python pandasai_visualization.py
|
| 87 |
+
# This will create a sample visualization using PandasAI
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
# API Keys
|
| 90 |
+
PANDAS_KEY=your-pandasai-key # Required for PandasAI visualization
|
| 91 |
+
GEMINI_API_KEY=your-gemini-api-key # For LLM query understanding
|
| 92 |
+
GEMINI_MODEL=gemini-2.0-flash-lite # LLM model selection
|
| 93 |
+
GEMINI_MODEL_PROVIDER=google_genai # LLM provider
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
# Path Configuration
|
| 96 |
+
MCP_SERVER_PATH=/absolute/path/to/postgre_mcp_server.py
|
| 97 |
+
TABLE_SUMMARY_PATH=table_summary.txt
|
| 98 |
+
```
|
| 99 |
|
| 100 |
+
## Running the Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 101 |
|
| 102 |
+
1. **Ensure PostgreSQL Database is Running:**
|
| 103 |
+
- Make sure your PostgreSQL instance is up and accessible
|
| 104 |
+
- Verify the connection details in `.env` are correct
|
| 105 |
|
| 106 |
+
2. **Start the Application:**
|
| 107 |
+
```bash
|
| 108 |
+
# Using the run script
|
| 109 |
+
chmod +x run.sh
|
| 110 |
+
./run.sh
|
| 111 |
|
| 112 |
+
# Or directly with Python
|
| 113 |
+
python gradio_app.py
|
| 114 |
+
```
|
| 115 |
|
| 116 |
+
3. **Access the Interface:**
|
| 117 |
+
- Open your browser to `http://localhost:7860`
|
| 118 |
+
- The chat interface will be ready for queries
|
| 119 |
|
| 120 |
+
## Usage
|
| 121 |
|
| 122 |
+
### Input Examples
|
| 123 |
|
| 124 |
+
Example prompts:
|
| 125 |
+
```
|
| 126 |
+
1. Simple queries:
|
| 127 |
+
"List all tables in the database"
|
| 128 |
+
"Show me the schema of table X"
|
| 129 |
|
| 130 |
+
2. Analysis queries:
|
| 131 |
+
"Count the number of active customers by region"
|
| 132 |
+
"Show me total sales by product category for the last month"
|
| 133 |
|
| 134 |
+
3. Visualization requests:
|
| 135 |
+
"Plot a bar chart showing sales distribution by region"
|
| 136 |
+
"Create a pie chart of customer segments"
|
| 137 |
+
```
|
| 138 |
|
| 139 |
+
### Output Structure
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
1. **Query Results:**
|
| 142 |
+
- Text results are displayed directly in the chat interface
|
| 143 |
+
- Tabular data is formatted as markdown tables
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
2. **Visualizations:**
|
| 146 |
+
- Generated charts are saved as PNG files in `./exports/charts/`
|
| 147 |
+
- Files are named with unique IDs: `temp_chart_{uuid}.png`
|
| 148 |
+
- Visualization is handled by the `visualize_results` MCP tool which:
|
| 149 |
+
* Automatically converts SQL results to pandas DataFrames
|
| 150 |
+
* Uses PandasAI to interpret visualization requests
|
| 151 |
+
* Generates appropriate chart types based on data and prompt
|
| 152 |
+
- Supports a wide range of visualization types:
|
| 153 |
+
* Bar charts for categorical comparisons
|
| 154 |
+
* Line plots for time series
|
| 155 |
+
* Pie charts for proportions
|
| 156 |
+
* Scatter plots for correlations
|
| 157 |
+
* And more based on data characteristics
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
### Response Format
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
The system provides responses in a structured format:
|
| 162 |
+
```markdown
|
| 163 |
+
# Result
|
| 164 |
+
[Query results in table or list format]
|
| 165 |
+
|
| 166 |
+
# Visualization (if requested)
|
| 167 |
+
[Path to generated visualization file]
|
| 168 |
+
|
| 169 |
+
# Explanation
|
| 170 |
+
[Brief interpretation of results]
|
| 171 |
+
|
| 172 |
+
# Query
|
| 173 |
+
```sql
|
| 174 |
+
[The executed SQL query]
|
| 175 |
+
```
|
| 176 |
+
```
|
| 177 |
|
| 178 |
## Project Structure
|
| 179 |
|
| 180 |
```
|
| 181 |
+
├── gradio_app.py # Main application and UI
|
| 182 |
+
├── postgre_mcp_server.py # Database server and tools
|
| 183 |
+
├── langchain_mcp_client.py # LangChain integration
|
| 184 |
+
├── conversation_memory.py # Memory management
|
| 185 |
+
├── utils.py # Helper utilities
|
| 186 |
+
├── pandasai_visualization.py # Visualization handling
|
| 187 |
+
├── requirements.txt # Project dependencies
|
| 188 |
+
├── run.sh # Run script
|
| 189 |
+
└── .env # Environment configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 190 |
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
exports/charts/temp_chart_5252d436-6dfe-46e3-a348-49308898940d.png
ADDED
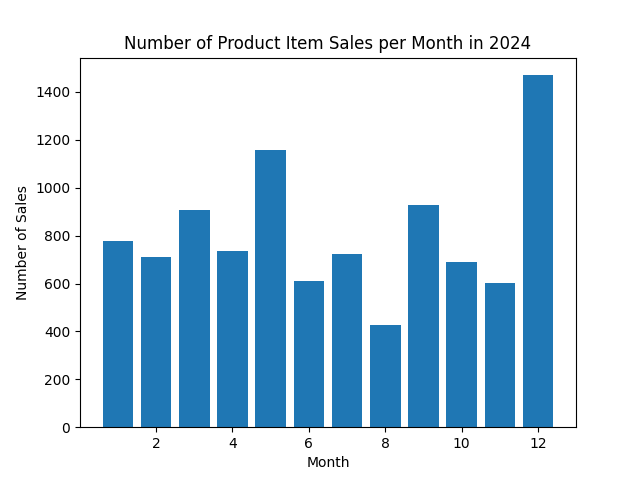
|
exports/charts/temp_chart_70308ee4-1919-43a6-b30a-c7024fb0440e.png
ADDED
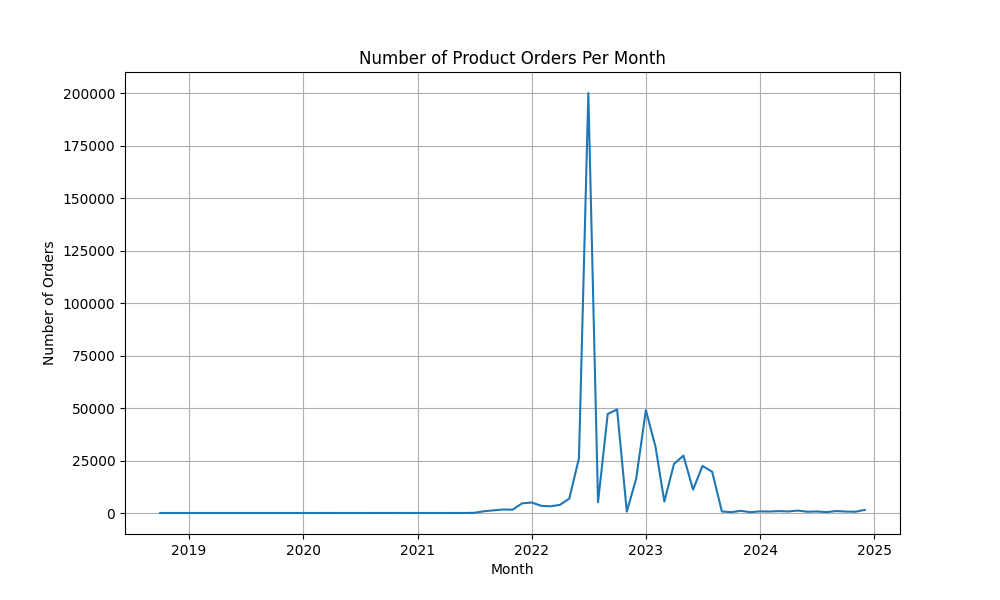
|
exports/charts/temp_chart_730e3451-365a-4a3f-9c4b-d95f991c4bbd.png
ADDED

|
exports/charts/temp_chart_7ee5d17e-a9a1-40e1-ab90-cc48a82ef03e.png
ADDED

|
exports/charts/temp_chart_91edd69e-ff3b-49e5-834b-399d57898523.png
ADDED
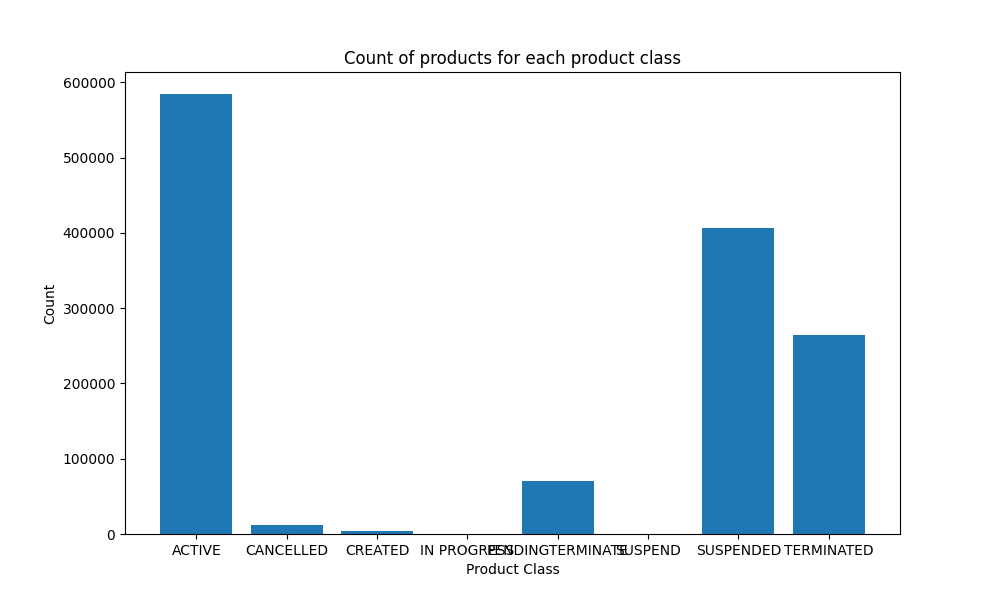
|
exports/charts/temp_chart_d2455884-7b1b-4dd5-8e9a-8d928ec9628b.png
DELETED
|
Binary file (17.5 kB)
|
|
|
gradio_app.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -34,6 +34,17 @@ demo = gr.ChatInterface(
|
|
| 34 |
type="messages",
|
| 35 |
flagging_mode="manual",
|
| 36 |
flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 37 |
save_history=True,
|
| 38 |
)
|
| 39 |
|
|
@@ -56,20 +67,9 @@ demo = gr.ChatInterface(
|
|
| 56 |
# flagging_mode="never"
|
| 57 |
# )
|
| 58 |
|
| 59 |
-
async def build_prompt(session, request, tools, table_summary):
|
| 60 |
-
conversation_prompt = await session.read_resource("resource://base_prompt")
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
tools_str = "\n".join([f"- {tool.name}: {tool.description}" for tool in tools])
|
| 64 |
|
| 65 |
-
return template.format(
|
| 66 |
-
new_request=request,
|
| 67 |
-
tools=tools_str,
|
| 68 |
-
descriptions=table_summary,
|
| 69 |
-
system_instructions="""You are a PostgreSQL database expert assistant.
|
| 70 |
-
Use the conversation history when available to maintain context.
|
| 71 |
-
For new conversations, focus on understanding the initial request."""
|
| 72 |
-
)
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 75 |
demo.launch()
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
type="messages",
|
| 35 |
flagging_mode="manual",
|
| 36 |
flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
|
| 37 |
+
# additional_outputs=[gr.Image(label="Visualization Output")],
|
| 38 |
+
examples=[
|
| 39 |
+
"List all tables in the database",
|
| 40 |
+
"Show me the schema of the dim_customer table",
|
| 41 |
+
"Count the number of active customers in 2024",
|
| 42 |
+
"Create a pie chart showing the distribution of customer statuses in the dim_customer table.",
|
| 43 |
+
"Plot a line chart showing the trend of order quantities over order dates from the dim_product_order_item table.",
|
| 44 |
+
"Generate a bar chart displaying the count of products in each product class from the dim_product table. Use beautiful and vivid colors fro visualization.",
|
| 45 |
+
"Visualize the relationship between tax_rate and tax_included_amount from the dim_product table using a scatter plot.",
|
| 46 |
+
"Visualize the number of product orders over time from the dim_product_order_item table, using the order_date. Show the trend monthly.",
|
| 47 |
+
],
|
| 48 |
save_history=True,
|
| 49 |
)
|
| 50 |
|
|
|
|
| 67 |
# flagging_mode="never"
|
| 68 |
# )
|
| 69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 70 |
|
| 71 |
+
# TODO: maybe we can add a mcp tool to validate the results (those converted to DataFrame) to make sure the valid type is passed to the visualization tool by ReAct agent
|
|
|
|
| 72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 75 |
demo.launch()
|
langchain_mcp_client.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -10,6 +10,10 @@ from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import FileChatMessageHistory
|
|
| 10 |
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
|
| 11 |
import logging
|
| 12 |
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
# Set up logging
|
| 15 |
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
|
| 11 |
import logging
|
| 12 |
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 13 |
+
from langchain.globals import set_debug
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
# set_debug(True)
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
# Set up logging
|
| 19 |
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
pandasai_visualization.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -24,11 +24,11 @@ from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
def create_sample_dataframe():
|
| 26 |
"""Create a sample dataframe with sales data."""
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
data = {
|
| 28 |
-
'Region': ['North', 'South', 'East', 'West', 'North', 'South', 'East', 'West'],
|
| 29 |
-
'Product': ['Widget', 'Widget', 'Widget', 'Widget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget'],
|
| 30 |
-
'Sales': [150, 200, 120, 180, 90, 110, 95, 130],
|
| 31 |
-
'Quarter': ['Q1', 'Q1', 'Q1', 'Q1', 'Q2', 'Q2', 'Q2', 'Q2'],
|
| 32 |
'Year': [2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023]
|
| 33 |
}
|
| 34 |
return pai.DataFrame(data)
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
def create_sample_dataframe():
|
| 26 |
"""Create a sample dataframe with sales data."""
|
| 27 |
+
# 'Region': ['North', 'South', 'East', 'West', 'North', 'South', 'East', 'West'],
|
| 28 |
+
# 'Product': ['Widget', 'Widget', 'Widget', 'Widget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget', 'Gadget'],
|
| 29 |
+
# 'Sales': [150, 200, 120, 180, 90, 110, 95, 130],
|
| 30 |
+
# 'Quarter': ['Q1', 'Q1', 'Q1', 'Q1', 'Q2', 'Q2', 'Q2', 'Q2'],
|
| 31 |
data = {
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
'Year': [2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023]
|
| 33 |
}
|
| 34 |
return pai.DataFrame(data)
|
postgre_mcp_server.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -9,10 +9,13 @@ from pydantic import Field
|
|
| 9 |
import pandasai as pai
|
| 10 |
import matplotlib as plt
|
| 11 |
import pandas as pd
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
# Constants
|
| 14 |
DEFAULT_QUERY_LIMIT = 100
|
| 15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
# Define our own PromptMessage class if the MCP one isn't available
|
| 18 |
@dataclass
|
|
@@ -65,14 +68,14 @@ async def base_prompt_query() -> str:
|
|
| 65 |
# Your Role
|
| 66 |
==========================
|
| 67 |
|
| 68 |
-
You are an expert in generating and executing SQL queries
|
| 69 |
|
| 70 |
- List available tables
|
| 71 |
- Retrieve schema details
|
| 72 |
- Execute SQL queries
|
|
|
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
Each tool may also return previews or summaries of table contents to help you better understand the data structure.
|
| 76 |
|
| 77 |
---
|
| 78 |
|
|
@@ -82,28 +85,15 @@ Each tool may also return previews or summaries of table contents to help you be
|
|
| 82 |
|
| 83 |
When a user submits a request, you must:
|
| 84 |
|
| 85 |
-
1. **Analyze the request** to determine the required data or
|
| 86 |
-
2. **Use FastMCP tools** to gather
|
| 87 |
3. **Generate a valid SQL SELECT query**, if needed, and clearly show the full query.
|
| 88 |
-
4. **Execute the SQL query** and return the results.
|
| 89 |
-
5. **
|
| 90 |
-
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
==========================
|
| 95 |
-
# Your Objective
|
| 96 |
-
==========================
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
When a user submits a request, follow these steps:
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
1. Analyze the request to determine the desired data or action.
|
| 101 |
-
2. Use tools to gather any necessary information (e.g., list tables, get schema).
|
| 102 |
-
3. Generate a valid SQL query (such as **SELECT**, **COUNT**, or other read-only operations) and clearly display the full query.
|
| 103 |
-
4. Execute the query and **return the execution result of the query**.
|
| 104 |
-
5. **Chain tools logically to build toward the answer.**
|
| 105 |
-
6. Explain your reasoning at every step for clarity and transparency.
|
| 106 |
-
7. Show the result of the **execute_query** in your final answer.
|
| 107 |
|
| 108 |
---
|
| 109 |
|
|
@@ -117,7 +107,11 @@ When a user submits a request, follow these steps:
|
|
| 117 |
- Validate SQL syntax before execution.
|
| 118 |
- Never assume table or column names. Use tools to confirm structure.
|
| 119 |
- Use memory efficiently. Don’t rerun a tool unless necessary.
|
| 120 |
-
- If you generate a SQL query, immediately call the **execute_query** tool
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 121 |
|
| 122 |
---
|
| 123 |
|
|
@@ -133,13 +127,12 @@ When a user submits a request, follow these steps:
|
|
| 133 |
# Tools
|
| 134 |
==========================
|
| 135 |
|
| 136 |
-
You can use the following FastMCP tools
|
| 137 |
|
| 138 |
{tools}
|
| 139 |
|
| 140 |
---
|
| 141 |
|
| 142 |
-
|
| 143 |
### Invalid Example — DELETE Operation (Not Allowed):
|
| 144 |
**User Request:** "Delete all customers from Germany."
|
| 145 |
|
|
@@ -161,21 +154,26 @@ Present your final answer using the following structure **exactly** in markdown
|
|
| 161 |
# Result
|
| 162 |
{{Take the result from the execute_query tool and format it nicely using Markdown. Use a Markdown table for tabular data (rows and columns) including headers. Use bullet points or items in markdown for answers that include lists of names or descriptions. Use plain text for single values or simple messages. Ensure data alignment and clarity.}}
|
| 163 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 164 |
# Explanation
|
| 165 |
-
{{Provide a concise explanation or interpretation of the results in 1-3 sentences. Explain what the data
|
| 166 |
|
| 167 |
# Query
|
| 168 |
```sql
|
| 169 |
{{Display the exact SQL query you generated and executed here to answer the user's request.}}
|
| 170 |
```
|
| 171 |
|
| 172 |
-
|
| 173 |
-
|
| 174 |
-
**
|
| 175 |
-
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
**
|
| 178 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 179 |
"""
|
| 180 |
|
| 181 |
return base_prompt
|
|
@@ -201,6 +199,7 @@ async def execute_query(
|
|
| 201 |
) -> str:
|
| 202 |
"""Execute a read-only SQL query against the database"""
|
| 203 |
# Validate query - simple check for read-only
|
|
|
|
| 204 |
query = query.strip()
|
| 205 |
if not query.lower().startswith("select"):
|
| 206 |
return "Error: Only SELECT queries are allowed for security reasons."
|
|
@@ -222,6 +221,16 @@ async def execute_query(
|
|
| 222 |
rows = [" | ".join(str(val) for val in row.values())
|
| 223 |
for row in result[:limit if limit else DEFAULT_QUERY_LIMIT]]
|
| 224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 225 |
return f"{header}\n{separator}\n" + "\n".join(rows)
|
| 226 |
except asyncpg.exceptions.PostgresError as e:
|
| 227 |
return f"SQL Error: {str(e)}"
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
import pandasai as pai
|
| 10 |
import matplotlib as plt
|
| 11 |
import pandas as pd
|
| 12 |
+
import logging
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
# Constants
|
| 15 |
DEFAULT_QUERY_LIMIT = 100
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
+
# logging info
|
| 18 |
+
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
# Define our own PromptMessage class if the MCP one isn't available
|
| 21 |
@dataclass
|
|
|
|
| 68 |
# Your Role
|
| 69 |
==========================
|
| 70 |
|
| 71 |
+
You are an expert in generating and executing SQL queries, interacting with a PostgreSQL database using **FastMCP tools**, and visualizing results when requested. These tools allow you to:
|
| 72 |
|
| 73 |
- List available tables
|
| 74 |
- Retrieve schema details
|
| 75 |
- Execute SQL queries
|
| 76 |
+
- Visualize query results using PandasAI
|
| 77 |
|
| 78 |
+
Each tool may return previews or summaries of table contents to help you understand the data structure.
|
|
|
|
| 79 |
|
| 80 |
---
|
| 81 |
|
|
|
|
| 85 |
|
| 86 |
When a user submits a request, you must:
|
| 87 |
|
| 88 |
+
1. **Analyze the request** to determine the required data, action, or visualization.
|
| 89 |
+
2. **Use FastMCP tools** to gather necessary information (e.g., list tables, retrieve schema).
|
| 90 |
3. **Generate a valid SQL SELECT query**, if needed, and clearly show the full query.
|
| 91 |
+
4. **Execute the SQL query** using the `execute_query` tool and return the results.
|
| 92 |
+
5. **Visualize results** using the `visualize_results` tool if the user explicitly requests a visualization (e.g., "create a chart", "visualize", "plot"). For visualizations:
|
| 93 |
+
- Craft a visualization prompt starting with "plot" (e.g., "plot a bar chart showing sales by region").
|
| 94 |
+
- Send JSON data in the format `{{'columns': [list of column names], 'data': [list of rows, each row a list of values]}}`.
|
| 95 |
+
6. **Chain tools logically**, such as: List Tables → Get Schema → Write and Run Query → Visualize Results (if requested).
|
| 96 |
+
7. **Explain your reasoning and each step taken** to ensure clarity and transparency.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 97 |
|
| 98 |
---
|
| 99 |
|
|
|
|
| 107 |
- Validate SQL syntax before execution.
|
| 108 |
- Never assume table or column names. Use tools to confirm structure.
|
| 109 |
- Use memory efficiently. Don’t rerun a tool unless necessary.
|
| 110 |
+
- If you generate a SQL query, immediately call the **execute_query** tool.
|
| 111 |
+
- If the user requests a visualization, call the **visualize_results** tool with:
|
| 112 |
+
- A visualization prompt starting with "plot" (e.g., "plot a bar chart showing sales by region").
|
| 113 |
+
- JSON data in the format `{{'columns': [list of column names], 'data': [list of rows, each row a list of values]}}`.
|
| 114 |
+
- For non-query or non-visualization requests (e.g., history questions), respond appropriately without forcing a query or visualization.
|
| 115 |
|
| 116 |
---
|
| 117 |
|
|
|
|
| 127 |
# Tools
|
| 128 |
==========================
|
| 129 |
|
| 130 |
+
You can use the following FastMCP tools to create **read-only** queries (e.g., `SELECT`, `COUNT`, `GROUP BY`, `ORDER BY`) and visualize results when requested. Chain tools logically to gather information, execute queries, or generate visualizations.
|
| 131 |
|
| 132 |
{tools}
|
| 133 |
|
| 134 |
---
|
| 135 |
|
|
|
|
| 136 |
### Invalid Example — DELETE Operation (Not Allowed):
|
| 137 |
**User Request:** "Delete all customers from Germany."
|
| 138 |
|
|
|
|
| 154 |
# Result
|
| 155 |
{{Take the result from the execute_query tool and format it nicely using Markdown. Use a Markdown table for tabular data (rows and columns) including headers. Use bullet points or items in markdown for answers that include lists of names or descriptions. Use plain text for single values or simple messages. Ensure data alignment and clarity.}}
|
| 156 |
|
| 157 |
+
# Visualization (if requested)
|
| 158 |
+
{{If the user requested a visualization, include the result from the visualize_results tool, e.g., "Visualization saved as visualization_output.png". Otherwise, omit this section.}}
|
| 159 |
+
|
| 160 |
# Explanation
|
| 161 |
+
{{Provide a concise explanation or interpretation of the results (and visualization, if applicable) in 1-3 sentences. Explain what the data and visualization (if any) represent in the context of the user's request.}}
|
| 162 |
|
| 163 |
# Query
|
| 164 |
```sql
|
| 165 |
{{Display the exact SQL query you generated and executed here to answer the user's request.}}
|
| 166 |
```
|
| 167 |
|
| 168 |
+
**Reminder:**
|
| 169 |
+
- **Every time you generate a SQL query, call `execute_query` immediately and include the result.**
|
| 170 |
+
- **If the user requests a visualization (e.g., "create a chart", "visualize", "plot"), call `visualize_results` with:**
|
| 171 |
+
- A visualization prompt starting with "plot" (e.g., "plot a bar chart showing sales by region").
|
| 172 |
+
- JSON data in the format `{{'columns': [list of column names], 'data': [list of rows, each row a list of values]}}`.
|
| 173 |
+
- **For non-query or non-visualization requests, respond appropriately without forcing a query or visualization.**
|
| 174 |
|
| 175 |
+
**Conversation History:**
|
| 176 |
+
Use the conversation history for context when available to maintain continuity.
|
| 177 |
"""
|
| 178 |
|
| 179 |
return base_prompt
|
|
|
|
| 199 |
) -> str:
|
| 200 |
"""Execute a read-only SQL query against the database"""
|
| 201 |
# Validate query - simple check for read-only
|
| 202 |
+
|
| 203 |
query = query.strip()
|
| 204 |
if not query.lower().startswith("select"):
|
| 205 |
return "Error: Only SELECT queries are allowed for security reasons."
|
|
|
|
| 221 |
rows = [" | ".join(str(val) for val in row.values())
|
| 222 |
for row in result[:limit if limit else DEFAULT_QUERY_LIMIT]]
|
| 223 |
|
| 224 |
+
# print(f"{header}\n{separator}\n" + "\n".join(rows))
|
| 225 |
+
|
| 226 |
+
# print(f"===== Header Type: ======\n {type(header)}")
|
| 227 |
+
# print(f"===== Row Type: ======\n {type(rows)}")
|
| 228 |
+
#
|
| 229 |
+
# # print the data itself
|
| 230 |
+
# print(f"===== Header Data: ======\n {header}")
|
| 231 |
+
# print(f"===== Row Data: ======\n {rows}")
|
| 232 |
+
|
| 233 |
+
|
| 234 |
return f"{header}\n{separator}\n" + "\n".join(rows)
|
| 235 |
except asyncpg.exceptions.PostgresError as e:
|
| 236 |
return f"SQL Error: {str(e)}"
|
visualization_output.png
DELETED
|
Binary file (17.5 kB)
|
|
|