Model Summary
NextTerm-47M is a pretrained transformer w/ 47.2M parameters, trained on 1.9 billion tokens of augmented data from the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS). It is designed to predict the next term in integer sequences. It displays exceptional in-context learning capabilities, and outperforms far larger generic LLMs on OEIS sequence completion tasks. It supports MLX and HuggingFace transformers.
The model is pretrained on sequences of up to length 1024, but can potentially generalize to longer sequences (this has not been extensively tested). All pretraining was done on a single RunPod H100 using MLX's CUDA backend. It is pretrained in float32. The model was trained for 335,000 steps with a batch size of 32 sequences, using Muon w/ a learning rate of 1e-2 and a fallback optimizer of AdamW with a learning rate of 1e-4. It uses the Qwen3 architecture with 12 layers, a model dimension of 512, 8 attention heads, and a feedforward dimension of 2048. It was trained using an estimated 540 exaFLOPs.
The model's tokenizer accepts integer sequences formatted as comma-separated values, e.g. "1,-2,3,-4,". The model outputs the next terms in the sequence in the same format. All non-digit, comma, or negative sign characters are ignored by the tokenizer. Note the model has not been trained on numbers with leading zeros, so inputs like "01,02,03," may yield unpredictable results as they are out-of-distribution. The model tokenizes digits individually, so larger integers will be represented by multiple tokens (e.g. "123" is tokenized as "1", "2", "3"). This means there is no magnitude limit on the integers the model can handle, but longer integers will consume more of the model's context window.
Inference Examples
Successful predictions by NextTerm-47M on various integer sequences:
1,2,3,4,5, -> 6,7,8,9,10,11,12,...
3,2,5,3,2,7,5,3,2,11,7,5,3, -> 2,13,11,7,5,3,2,17,...
10001,10010,10100, -> 11000,100001,100010,100100,101000,110000,1000001,...
123,456,789,101112, -> 131415,161718,192021,222324,252627,282930,...
3,9,4,16,5, -> 25,6,36,7,49,8,64,...
Not all predictions are successful; example failure case below:
3,9,7,49,8,64,10,100,15, -> 121,14,144,16,169,21,196,... (fails to identify square in-context)
Evaluation Results
Arithmetic Evaluation
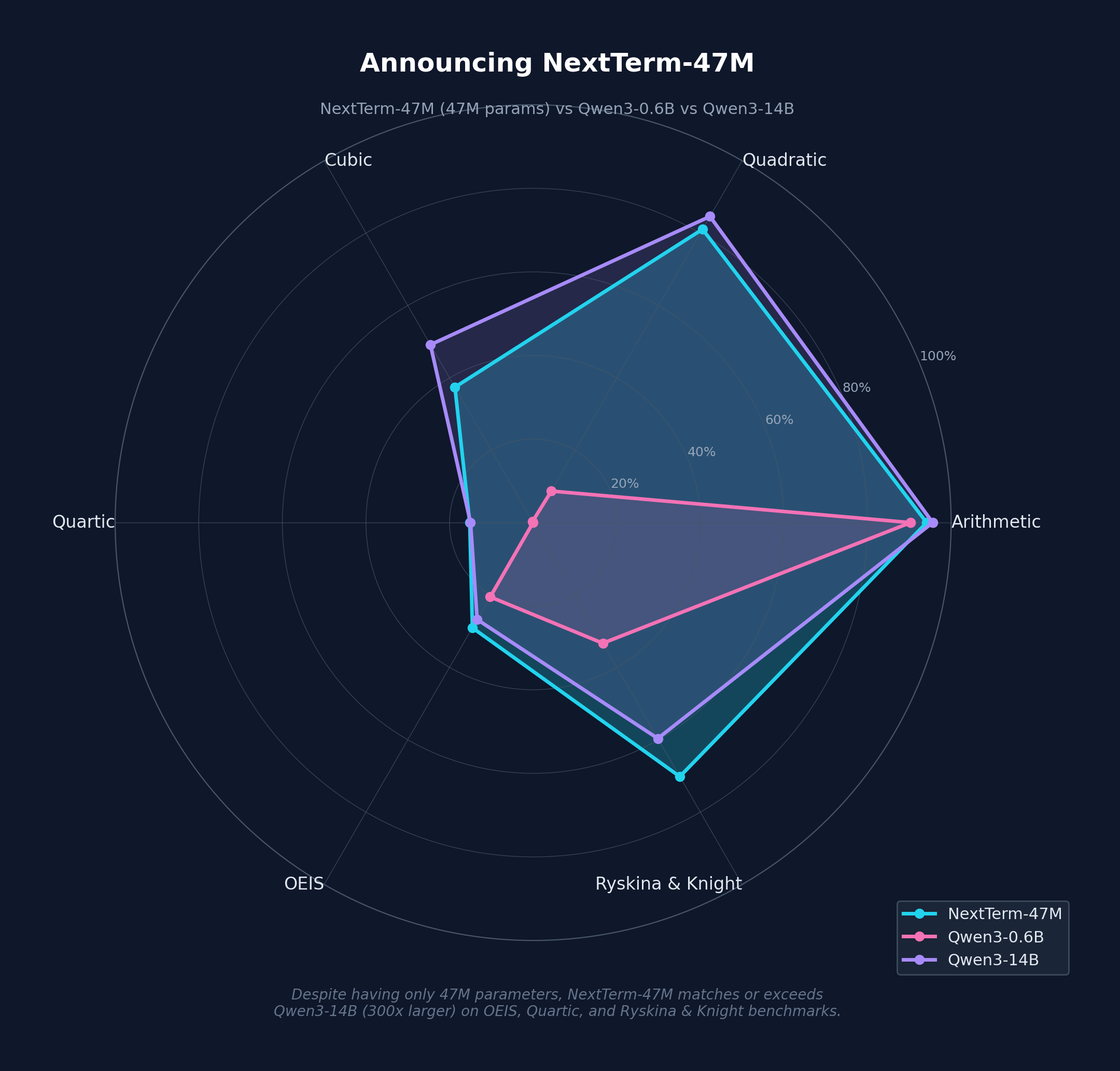
The arithmetic evaluation consists of predicting the next term in sequences generated by polynomial functions of varying degrees (arithmetic, quadratic, cubic, quartic), across varying shot counts. The models are evaluated based on the accuracy of their predictions, w/ exact-match. NextTerm-47M outperforms all Qwen models <4B, though larger Qwen models do better on lower-degree polynomials.
| Model | Arithmetic | Quadratic | Cubic | Quartic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NextTerm-47M | 94.15% | 81.07% | 37.43% | 15.17% |
| Qwen3-0.6B | 90.31% | 8.72% | 0.30% | 0.02% |
| Qwen3-1.7B | 93.10% | 41.57% | 5.36% | 0.71% |
| Qwen3-4B | 93.90% | 77.26% | 28.18% | 5.98% |
| Qwen3-8B | 96.10% | 80.59% | 32.93% | 7.95% |
| Qwen3-14B | 95.60% | 84.61% | 49.16% | 14.98% |
OEIS Evaluation
This consists of predicting the next term in real OEIS sequences from a held-out, decontaminated validation set. Note that the NextTerm model is the only one guaranteed to not have seen any of these sequences during training. NextTerm-47M outperforms all Qwen models, including the largest 14B parameter model.
| Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| NextTerm-47M | 29.06% |
| Qwen3-0.6B | 20.53% |
| Qwen3-1.7B | 22.65% |
| Qwen3-4B | 24.95% |
| Qwen3-8B | 25.78% |
| Qwen3-14B | 26.78% |
Ryskina & Knight (2021)
This evaluation consists of predicting the next term in 57 sequences from Ryskina & Knight (2021). These sequences were compiled to evaluate OEIS-style sequence completion. NextTerm-47M outperforms all other models. Note that this evaluation has not been decontaminated for Qwen or NextTerm-47M, so some sequences may have been seen during training by some models.
| Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| NextTerm-47M | 70.18% |
| OEIS-LSTM | 5% |
| GPT-2 | 7% |
| OEIS Lookup | 53% |
| Qwen3-0.6B | 33.33% |
| Qwen3-1.7B | 49.12% |
| Qwen3-4B | 63.16% |
| Qwen3-8B | 57.89% |
| Qwen3-14B | 59.65% |
Reproducibility
The code used to evaluate the model on these benchmarks can be found here. This repository includes the evaluation scripts, as well as the script enhance_data.py used to generate the augmented training data from OEIS. Augmentations include affine transformations, partial summation, subsampling, permuting, etc. The enhanced dataset itself can be found at N8Programs/oeis-enhanced, in the oeis_train_uber_shuffled.jsonl file.
Note that of all checkpoints produced during training, the one with the lowest validation loss was used for this model card and the evaluation results above. This may slightly inflate the reported performance, but the difference is expected to be minimal. For transparency and testing, all checkpoints produced during training are available at N8Programs/NextTerm-47M-Checkpts.
Usage
MLX:
mlx_lm.generate --model N8Programs/N8Programs/NextTerm-47M-Checkpts --prompt "1,2,3"
HuggingFace Transformers:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
# Load the model and tokenizer
model_name = "N8Programs/NextTerm-47M"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Prompt the model
prompt = "1,2,3,4,5,"
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
# Generate output
outputs = model.generate(inputs["input_ids"], max_new_tokens=5000)
result = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"Prompt: {prompt}")
print(f"Output: {result}")
Citation
If you use this model in your research, please cite it as follows:
@misc{nextterm47m2025,
author = {Nathan Breslow},
title = {NextTerm-47M: A Pretrained Transformer for Integer Sequence Prediction},
year = {2025},
publisher = {Hugging Face},
howpublished = {\url{https://huggingface.co/N8Programs/NextTerm-47M}},
note = {47.2M parameter model trained on augmented OEIS data}
}
Attribution
This model and dataset were trained and created using data from the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS).
- Source: https://oeis.org/
- License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 (CC BY-SA 4.0)
- OEIS End-User License Agreement: https://oeis.org/wiki/The_OEIS_End-User_License_Agreement
- Downloads last month
- 42