📷 CAMS: A Large-Scale, Multi-faceted, Attribute-based Chinese Summarization Dataset
💻 Github Repo
简体中文 | English
Introduction
CAMS (Chinese Attribute-based Multi-faceted Summarization) is a large-scale Chinese summarization dataset designed to advance research in long-document summarization. With the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), high-quality, large-scale training data has become crucial, especially for non-English languages. CAMS aims to fill the gap in the field of Chinese long-text summarization.
The dataset contains 1 million high-quality, long Chinese articles. Each article is paired with three summaries of different granularities and a rich set of attribute labels.
Key Features
- Focus on Long Documents: The articles in the dataset have an average length of over 1,500 characters, providing a challenging platform for training and evaluating long-text summarization models.
- Multi-Level Summaries: Each article comes with three hierarchically structured summaries:
- Long Summary: A detailed and comprehensive summary covering the key information of the original text.
- Medium Summary: A concise overview of the article's core points.
- Short Summary: A one-sentence summary of the article's central idea.
- Rich Attribute Annotations: Each article has been annotated with multi-dimensional attributes, including:
- Keywords
- Statement Type: Factual Statement vs. Opinion Expression
- Sentiment: Positive, Somewhat Positive, Neutral, Somewhat Negative, Negative
- Formality: Formal vs. Colloquial
- Tense: Past, Present, Future
We hope the CAMS dataset will foster research and innovation in areas such as controllable summarization, attribute-aware generation, and long-text understanding.
📊 Data Statistics
Basic Information
To better illustrate the basic statistics of CAMS, we compare it with other mainstream Chinese and English summarization datasets.
| Dataset | Size | Avg. Doc Length | Avg. Summary Length | Avg. #Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | ||||
| NYT | 655K | 552.1 | 42.8 | - |
| CNNDM | 312K | 791.7 | 55.2 | - |
| Newsroom | 1.0M | 765.6 | 30.2 | - |
| Chinese | ||||
| LCSTS | 2.4M | 103.7 | 17.9 | - |
| CLTS | 185K | 1363.7 | 58.1 | - |
| CNewSum | 396K | 730.4 | 35.1 | - |
| CSL | 396K | 206.0 | 19.0 | 5.1 |
| CAMS | 1.0M | 1571.4 | 60.0 (S) 185.7 (M) 428.1 (L) |
14.3 |
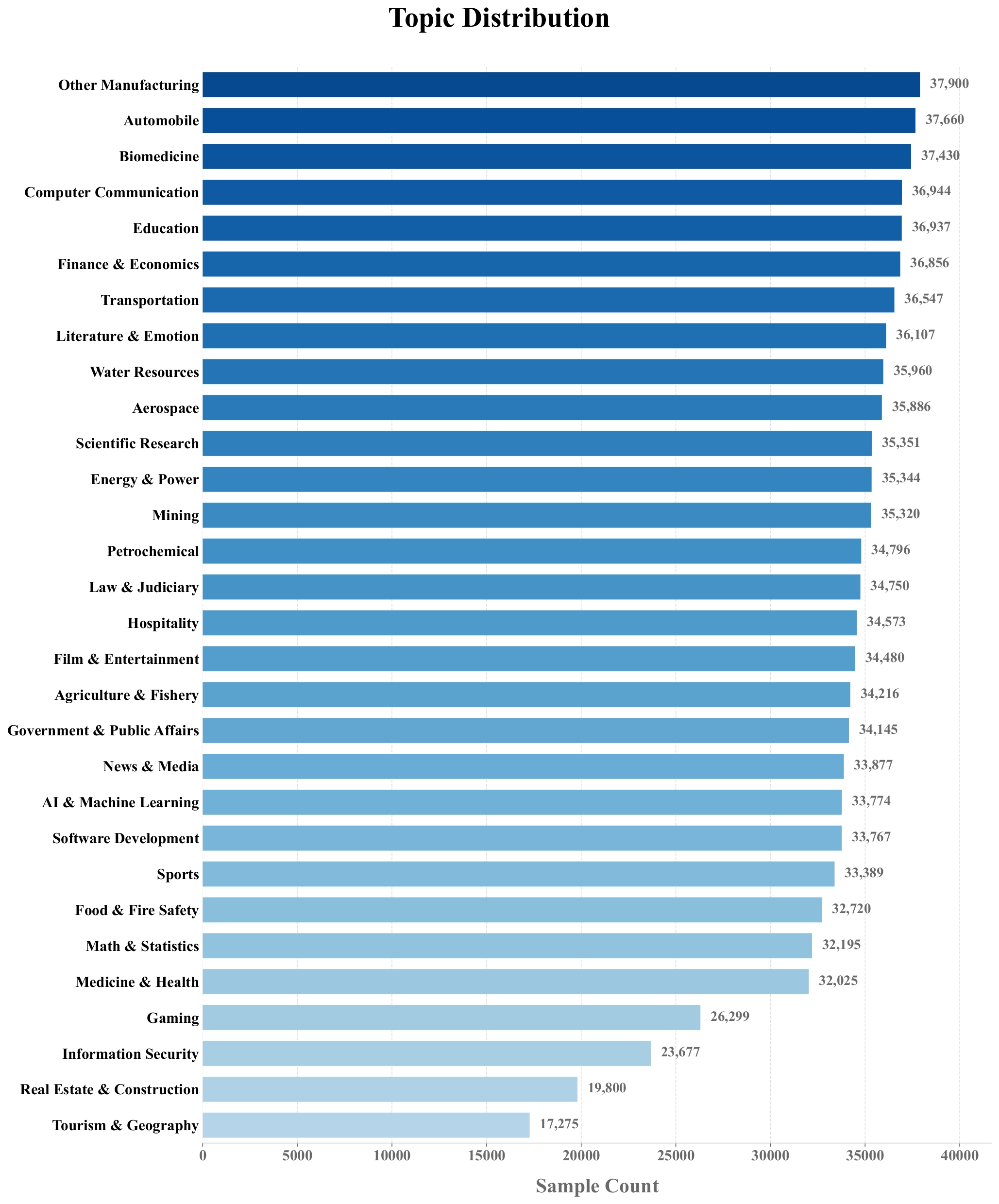
Topic Distribution
CAMS covers 30 distinct topics, where the key is the field name in the dataset and the value is the topic content:
{
"other_manufacturing": "Other Manufacturing",
"automobile": "Automobile",
"biomedicine": "Biomedicine",
"computer_communication": "Computer Communication",
"subject_education_education": "Education",
"finance_economics": "Finance & Economics",
"transportation": "Transportation",
"literature_emotion": "Literature & Emotion",
"water_resources_ocean": "Water Resources",
"aerospace": "Aerospace",
"technology_scientific_research": "Scientific Research",
"electric_power_energy": "Energy & Power",
"mining": "Mining",
"petrochemical": "Petrochemical",
"law_judiciary": "Law & Judiciary",
"accommodation_catering_hotel": "Hospitality",
"film_entertainment": "Film & Entertainment",
"agriculture_forestry_animal_husbandry_fishery": "Agriculture & Fishery",
"current_affairs_government_administration": "Government & Public Affairs",
"news_media": "News & Media",
"artificial_intelligence_machine_learning": "AI & Machine Learning",
"computer_programming_code": "Software Development",
"sports": "Sports",
"fire_safety_food_safety": "Food & Fire Safety",
"mathematics_statistics": "Math & Statistics",
"medicine_health_psychology_traditional_chinese_medicine": "Medicine & Health",
"game": "Gaming",
"other_information_services_information_security": "Information Security",
"real_estate_construction": "Real Estate & Construction",
"tourism_geography": "Tourism & Geography"
}
The topic distribution of the samples is as follows:
We also extracted a subset of samples, obtained their text embeddings, and visualized the topic distribution using UMAP for dimensionality reduction:
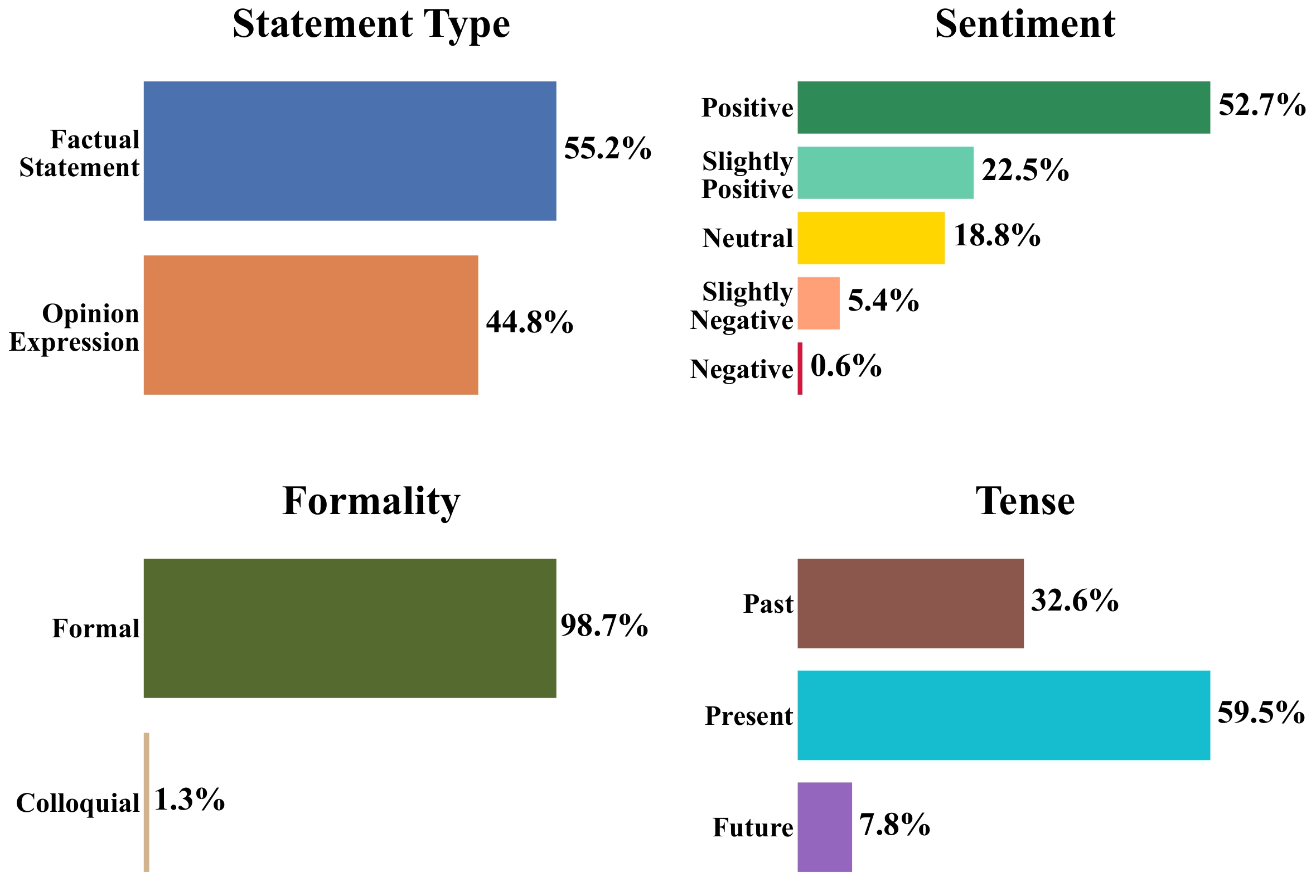
Attribute Annotation
The distribution of the four additional attribute annotations is shown below:
📂 Data Format
Each sample in the dataset is stored in JSON format and contains the following fields:
{
"id": "A unique identifier for each data entry",
"text": "The original content of the article",
"topic": "The topic of the article",
"short_summary": "A one-sentence short summary",
"medium_summary": "A medium-length summary",
"long_summary": "A detailed long summary",
"keywords": ["Keyword1", "Keyword2", "Keyword3", "..."],
"statement_type": "The type of statement (e.g., factual vs. opinion)",
"sentiment": "The sentiment of the article or the author's stance",
"formality": "The formality of the article's writing style",
"tense": "The tense of the article",
}
🛠️ Dataset Construction
The construction of CAMS was divided into three main stages:
Data Source and Preprocessing: We started with approximately 10 million articles from a large-scale, high-quality corpus, IndustryCorpus2, as our initial candidate set. After rigorous quality filtering, heuristic-based filtering, and topic-balanced resampling, we curated a final set of 1 million high-quality, topically diverse articles.
Multi-Level Summary Generation: We proposed a Stepwise Generation pipeline. This process first generates a detailed long summary from the original article. Then, it uses both the original article and the long summary as context to generate the medium summary. Finally, it combines the article, long summary, and medium summary to produce the most concise short summary. This method ensures consistency and coherence across the different levels of summaries.

Multi-faceted Attribute Annotation: For each article, we performed keyword extraction and annotated multiple linguistic and stylistic attributes. We employed a multi-round generation and voting mechanism to ensure the accuracy of these annotations.
🚀 Usage Example
You can easily load the CAMS dataset using the 🤗 datasets library.
from datasets import load_dataset
# Load the CAMS dataset
dataset = load_dataset("Mxode/CAMS")
# Inspect the dataset structure
print(dataset)
# Access the first sample
sample = dataset["train"][0]
print("Article:", sample["text"][:200])
print("Short Summary:", sample["short_summary"])
print("Keywords:", sample["keywords"])
📜 Citation
If you use the CAMS dataset in your research, please cite our work:
@misc{zhang2025CAMS,
title={CAMS: A Large-Scale Chinese Attribute-based Multi-faceted Summarization Dataset},
url={https://huggingface.co/datasets/Mxode/CAMS},
author={Xiantao Zhang},
month={August},
year={2025}
}
📄 License
This dataset is licensed under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license.